HTML revisions. Consolidation. Coordinate systems, units/scales, geometric entities, visualization (perspective). Modeling and editing of solids and surfaces (Platonic solids), use of the Autocad program.
Tetaedro
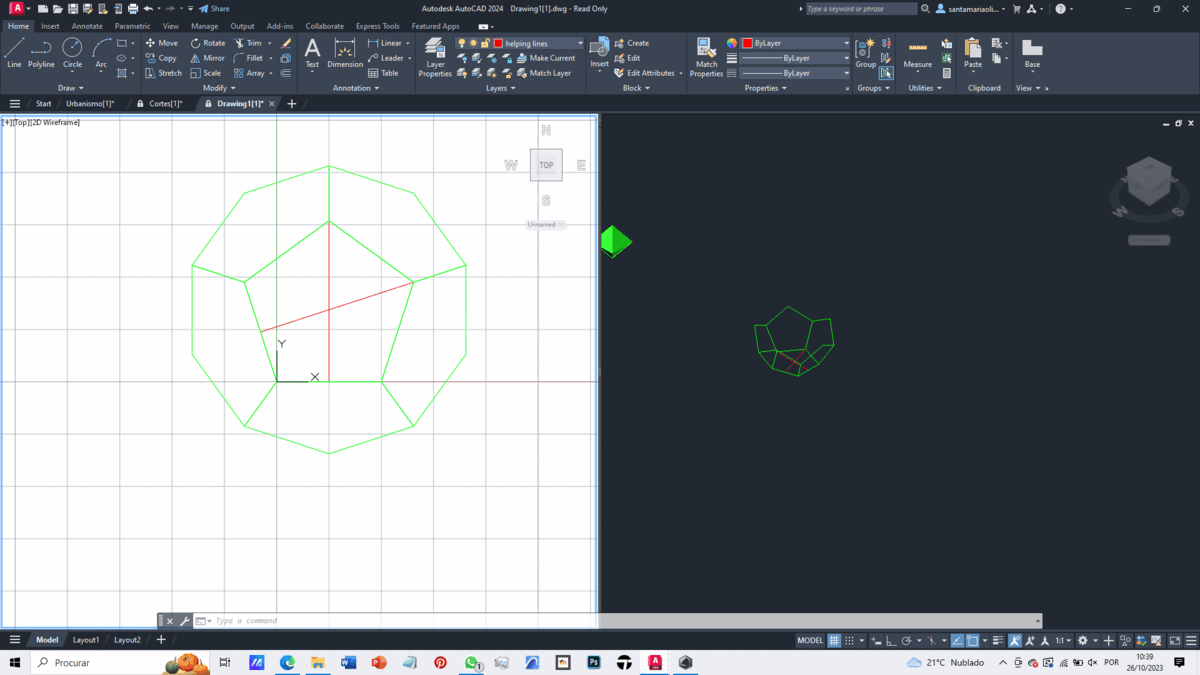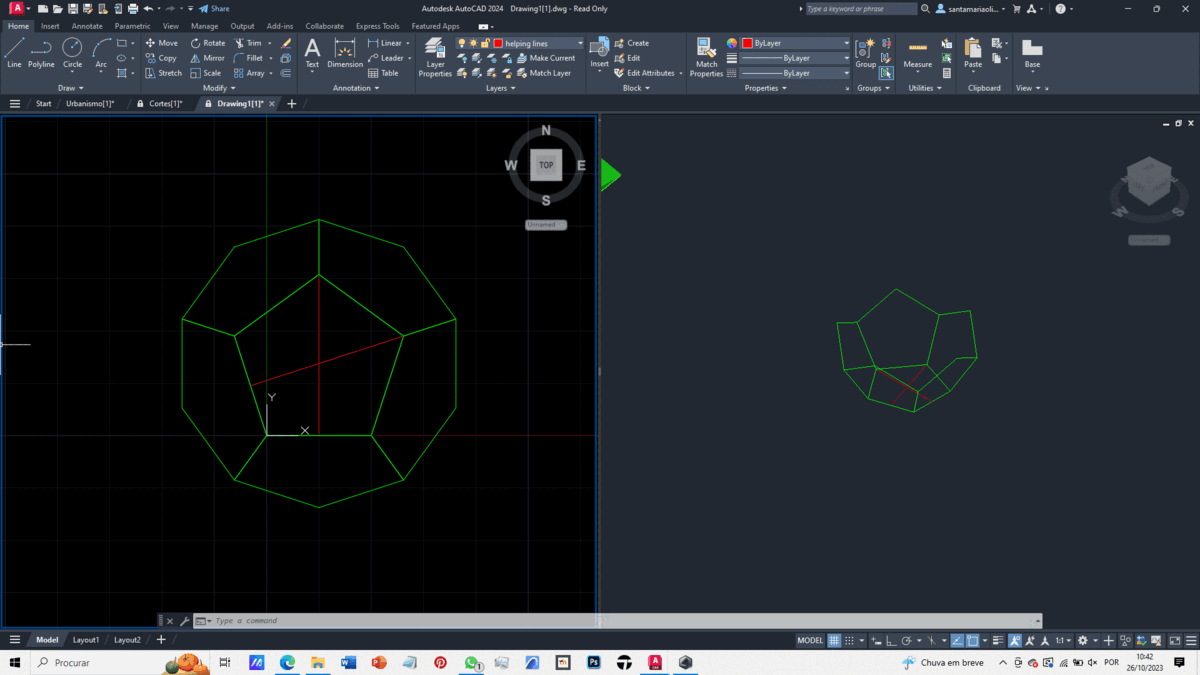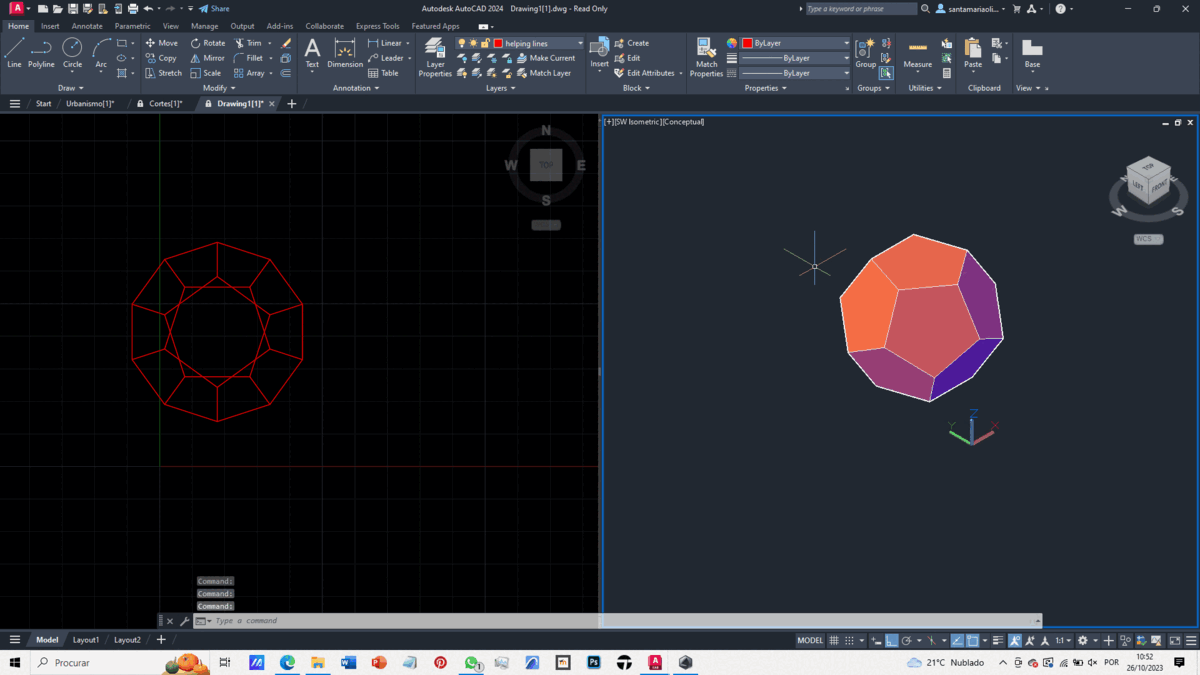
To create our solid, we import the file without units and use two views, one 2D and the other isometric.
With this foundation, we create 3 polygons with 5 sides each to form the base of our dodecahedron. We use various auxiliary lines and a circle for the rotation of one of the faces at the correct angle—this involves geometric considerations.
To rotate the faces of the pyramid, we need to change the orientation of the axes. Using the UCS command, we can edit these orientations, allowing us to rotate the face appropriately.
Using the Polar Array command, we copy the completed face and duplicate it around the base face of our octahedron.
With half of the dodecahedron complete, we duplicate it, and using the Align command, we join the two halves together.
The final result is depicted in the GIF.
Isocaedro
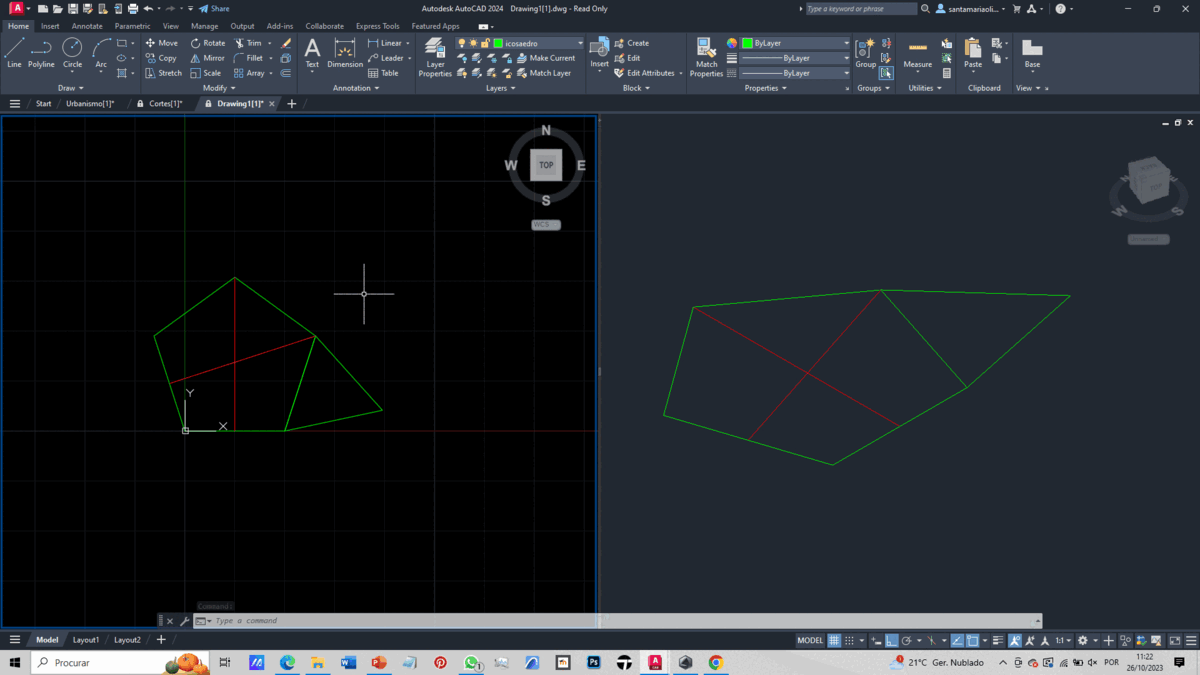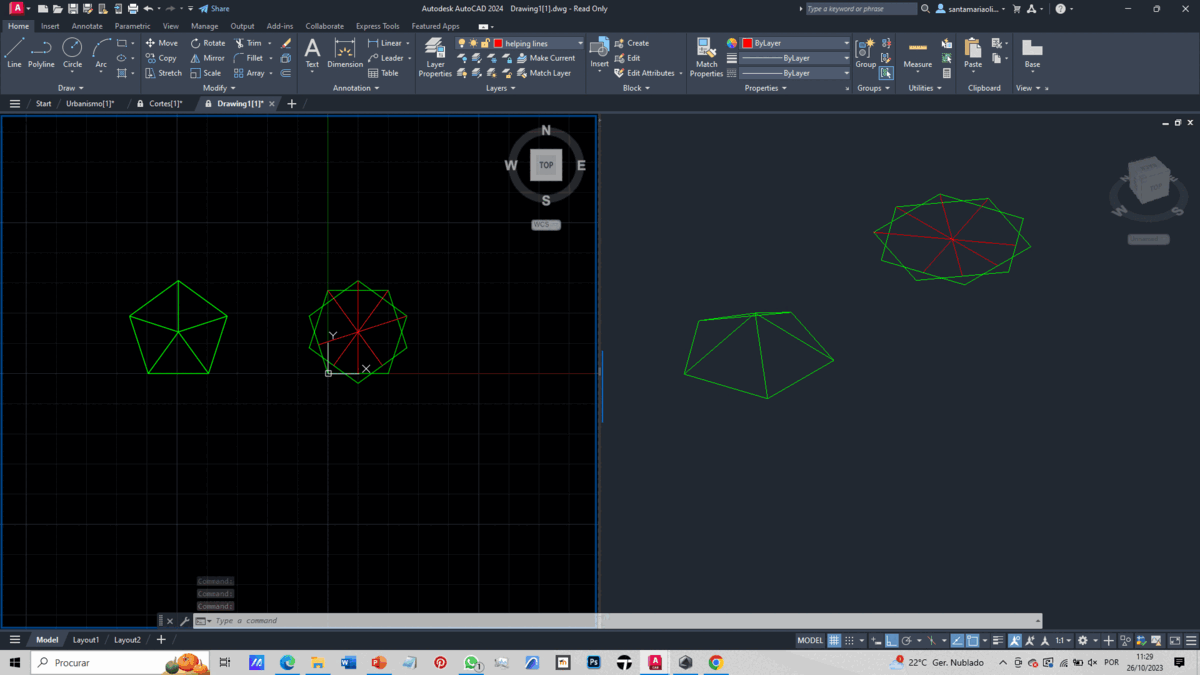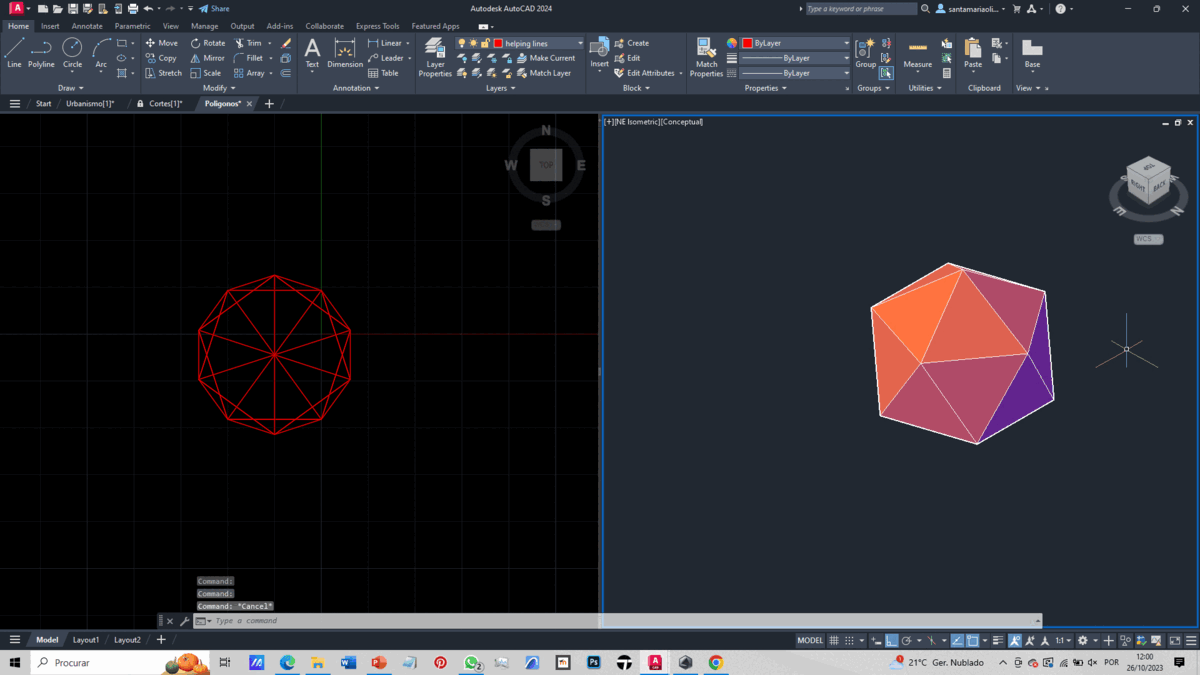
To create our solid, we import the file without units and use two views, one 2D and the other isometric.
With this foundation, we create 1 polygon with 5 sides to form the base and 5 other polygons with 3 sides each, using the "polygon" command, to create a pentagonal pyramid. We generate a circle passing through a vertex of a triangle, with its center at the midpoint of an edge of the pentagon. Additionally, we create a vertical line from the center of the pentagon.
To rotate the faces of the pyramid, we need to change the orientation of the axes. Using the UCS command, we can edit these orientations, allowing us to rotate each face with a specific axis orientation at the intersection of the circle and the vertical line.
Using the Polar Array command, we copy the completed face and duplicate it around the pentagon.
By creating two pentagons, one on top of the other with a 36-degree difference, we form a base. We then create triangles around this base using geometry and the Polar Array command. This part is then combined with the previously made pentagonal pyramid.
With half of the icosahedron complete, we duplicate it, and using the Align command, we join the two halves together.
The final result is depicted in the GIF.
Dado
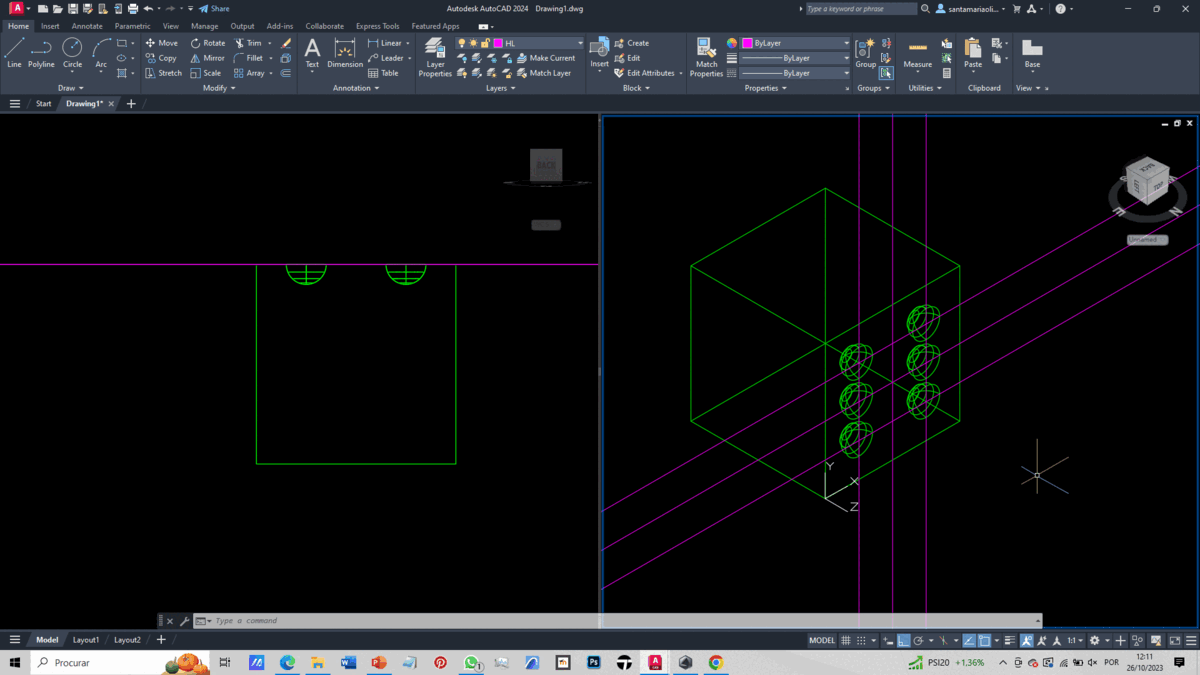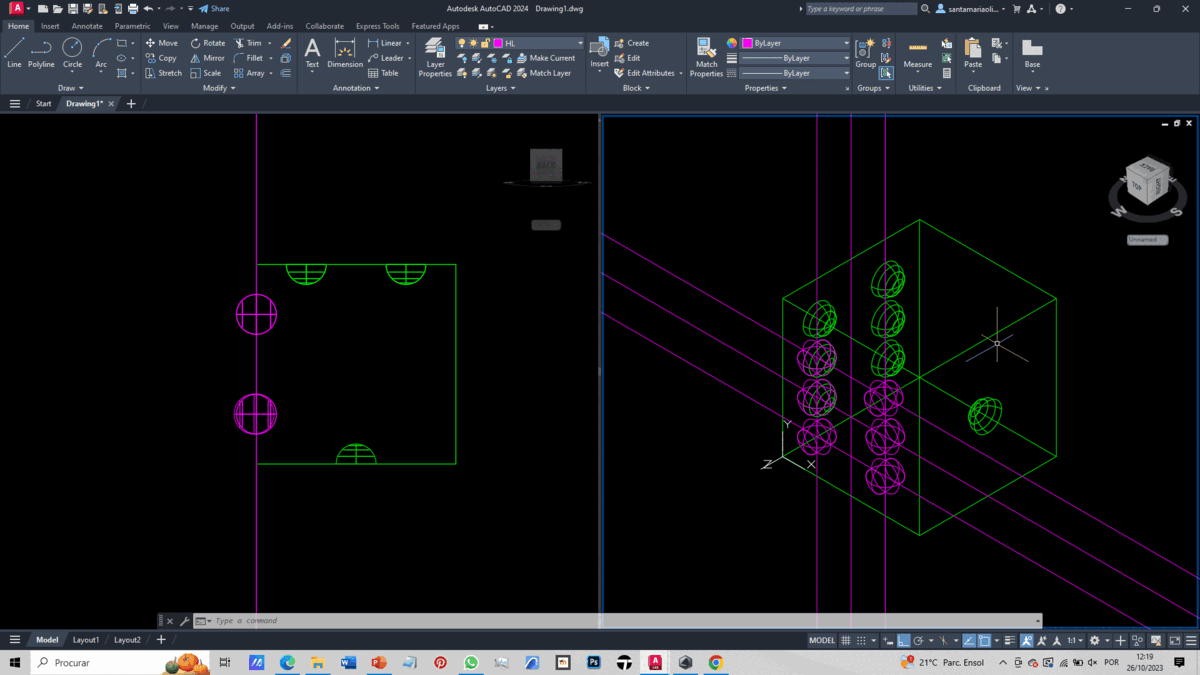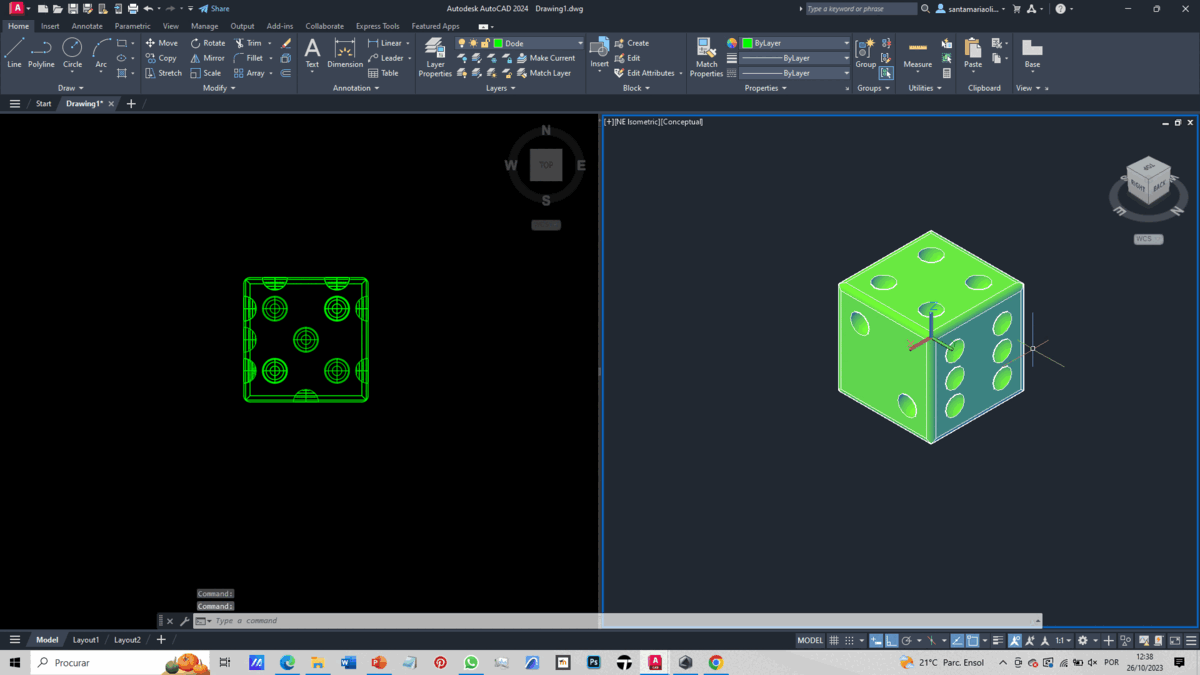
To create our solid, we import the file without units.
With this foundation, we create a box, which forms the base of our die. Using the Xlines command, we draw auxiliary lines passing through the midpoints of two adjacent edges on the same face.
From these lines, we create parallel lines spaced 2.5 units apart using the Offset command. Subsequently, we generate spheres at the intersection of these lines using the Sphere command, creating as many spheres as there are points on the face's side.
Using the Subtraction command, we subtract the spheres from the box, obtaining the void of the spheres. We repeat this process for the remaining faces. With this phase completed, we round the edges of all faces using the Fillet command.
The final result is depicted in the GIF.